NEWS DETAILS
What is uninterruptible power supply? Why is it essential to modern infrastructure?
Digital era: Sudden power failures cause data loss, production/communication disruptions — downtime carries massive costs. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) are thus the cornerstone of continuous operations. This paper focuses on UPS systems, highlighting robust solutions (three-phase UPS, low-frequency UPS) and the specific role of dedicated telecom UPS.

What is the Uninterruptible Power Source.
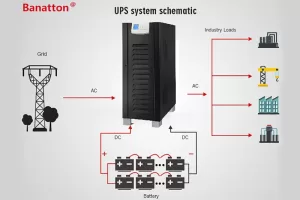
Uninterruptible power supply or uninterruptible power supply is an electrical device that provides emergency power to a load when the input power supply (usually the mains power supply) fails. However, uninterruptible power supply is not just a backup battery. Its main functions is:
1. Voltage regulation and filtering: It eliminates voltage drop (sudden drop) and surge (peak) and provides clean and stable power supply for connected equipment.
2. Surge Protection: It can protect sensitive electronic equipment from the impact of lightning or power grid switching caused by surges.
3. Standby Power supply: When the power is completely cut off, it will immediately switch to the internal batteries, so that it can continue to run or be automatically turned off.
4. Frequency stability: It is especially important for sensitive equipment, which can maintain a consistent electrical frequency.
The core principle is to act as a buffer between the unreliable power grid and your critical load, ensuring uninterrupted high-quality power.
The unique advantages of high reliability three-phase UPS.
While small, single-phase UPS units are common for protecting individual workstations, industrial and commercial facilities require the robustness of a Three Phase UPS. These systems are specially designed for high-power applications and have obvious advantages rooted in the concept of high reliability.
High reliability design: the core advantage lies in a design of separation of main input power supply and bypass power supply. This allows two independent main power lines to be connected to the UPS, thus forming a dual power input, which significantly improves the reliability of the output power. The double-conversion on-line topology (continuously converting AC power supply to DC and then back to clean AC power supply) can provide pure sinusoidal power supply, with functions of frequency tracking, phase locking, voltage regulation and noise filtering. This makes the equipment almost unaffected by all the power grid fluctuations, providing comprehensive protection. According to a report by the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI), power quality problems cause more than $ 150 billion in losses to American companies every year. [Source: https://www.epri.com/] a robust Three Phase UPS is a direct defense against these losses.
High battery optimization: battery health is crucial. Advanced systems adopts intelligent battery management (ABM) technology, which can prolong battery life and reduce maintenance work. Coupled with advanced constant current automatic charging, this technology maximizes the efficiency of the battery, shortens charging time, significantly prolongs the overall life cycle of the battery and reduces the total cost of ownership.
Strong Redundancy and Capacity Parallel Capability: For mission-critical applications, a single point of failure is unacceptable. By inserting an optional parallel module, a high-end UPS system can be connected in parallel, with up to eight or more units. This produces an n+1 redundant system; If one unit fails, other units will share the load seamlessly and without interruption. The system uses a non-fixed master-slave relationship, which means that the first power-on unit acts as the master unit, but roles can be exchanged, thus enhancing the flexibility and stability of the system.
Energy saving and environmental protection design: the design of modern UPS systems considers efficiency. Intelligent fan speed control (adjusted according to load and temperature) and non-circulating control circuit can ensure excellent heat dissipation and high energy efficiency. The use of green rectification and inverter technologies provides users with clean energy, while minimizing power waste.
Low-frequency UPS and high-frequency UPS: an important difference.
When choosing three-phase UPS, you will encounter two basic design concepts: low frequency UPS and high frequency UPS. The characteristic of low frequency UPS is that it has a huge insulation transformer inside. This design has several inherent advantages.
Robustness and Durability: The transformer provides superior electrical isolation and can withstand heavy transient overloads, making the Low Frequency UPS ideal for harsh industrial environments.
Strong Current Impact Capability: It can handle the high inrush currents required to start large motors or pumps without strain.
Longer Operational Life: the simpler, sturdier design often translates to a longer service life, typically 15-20 years, compared to high-frequency models.
While high-frequency Ups are smaller and more efficient at light loads, the Low Frequency UPS remains the gold standard for applications where maximum resilience and the ability to handle difficult loads are non-negotiable.
Main application scenarios and functions of UPS for private telecommunications.
Reliable uninterruptible power supply system has a wide range of applications. They are essential in the following aspects:
Industrial Processes: Protect manufacturing and control systems, industrial machinery and process monitoring from power events, which could lead to costly defects or production stoppage.
Critical Infrastructures: Ensuring continuous operation in hospitals, data centers, airports, water treatment plants, and power plants. A study by the Ponemon Research Institute found that the average cost of a data center downtime reaches $ 9,000 per minute [Source: https://www.ponemon.org/]
Energy Industry: ensuring the safe operations of oil and gas, petrochemical and mining facilities.
Military Applications: providing safe and clean power supply for sensitive command, control and communication systems.
Telecommunication is a typical example in these industries. Telecom UPS is designed to meet the specific requirements of telecom infrastructure, such as central offices and cellular towers. These systems usually have a wide input voltage range, are compatible with -48 V DC battery factory commonly used in the telecommunications industry, and have a robust designs for reliable operation under various environmental conditions, thus ensuring that communication networks remains online when the power grid is unstable.
Frequently asked Questions and answers
Q: Are all UPS systems equipped with built-in batteries?
A: No, it depends on the customer’s load and latency requirements.
Q: What certifications are important?
A: Look for safety marks like the CE certificate, indicating compliance with European health, safety, and environmental standards.
Q: How long can UPS be used before it is replaced?
A: Most UPS units can be used for 3-5 years. Depending on usage and environment, the batteries may need to be replaced sooner.
Sum up
Choosing the right uninterruptible power supply needs to know the specific requirements. Three-phase UPS ensures reliability for high-power applications, low-frequency UPS provides stability for industrial environment, and telecom UPS meets special communication requirements. Investing in the proper Uninterruptible Power Source protects operations against power disruptions, ensuring business continuity.
Related Articles
The Power of Modular UPS Systems in Commercial Infrastructure
What is an industrial UPS?—How to choose an industrial UPS?
The Development of Voltage Stabilizers
Posts Categories
- News23