FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is an Offline UPS?
When the mains power is normal, the mains power is supplied to the devices through simple voltage stabilization and filtering, while the battery is charged. During a power outage, the inverter operates, converting the DC power provided by the battery into stable AC power for the devices. Since the inverter is idle during normal mains power conditions and only operates when the battery is discharged during a mains power outage, this type of UPS is called a offline UPS.
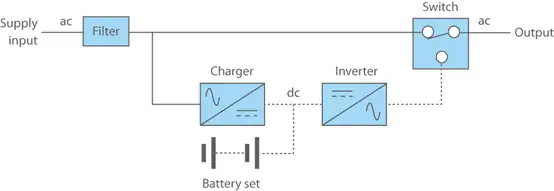
Advantages
Compact size, high efficiency, low price, and low operating costs. Since the inverter is idle during normal conditions, grid power is directly supplied to the load, resulting in a high power conversion efficiency.
Disadvantages
The load is not truly isolated from the mains power system; the long transfer time and lack of a true static switch mean that transferring the load to the inverter takes a relatively long time. While this transfer time is acceptable in some applications (such as a single computer), it is not sufficient for large or complex sensitive loads (such as large computer centers and telephone exchanges). The output voltage cannot be adjusted, and the output frequency depends on the frequency of the AC input power and cannot be adjusted.
Offline UPS are primarily suitable for applications where mains power fluctuations are minimal and power quality requirements are low. With a switching time typically less than 10 milliseconds, offline UPS are unsuitable for critical applications where power cannot be interrupted. However, this switching time is actually quite short. The switching power supplies in typical computers and other electrical equipment should maintain a power supply of approximately 10 milliseconds during a power outage, so this switching time generally does not cause any problems for the equipment.
Q2: What is a UPS?
UPS (Uninterruptible Power System): An “uninterruptible power supply” consists of a battery pack, inverter, and control circuit. It provides uninterrupted AC power protection and energy storage equipment during grid anomalies (power outages, surges, undervoltage, mains brownouts, radiation interference, etc.).

Q3: What is a Modular UPS?
A modular UPS is a highly flexible and scalable uninterruptible power supply (UPS).
The modular UPS system architecture is highly flexible. The power modules are designed to be easily removed and installed during operation without affecting system performance or output. This allows investment planning to be “scalable on demand” and users to achieve “dynamic growth” as their business evolves. This not only allows for future equipment expansion, but also reduces initial acquisition costs. It is widely used in various scenarios requiring high reliability and flexible expansion, such as data centers, computer rooms, telecommunications base stations, financial trading centers, traffic control centers, and medical equipment.
10 benefits of Modular UPS
1.REDUNDANCY
2.LOWER COST OF INSTALLATION
3.LOWEST FLOOR SPACE, COMPARED TO OTHER SCALABLE / PARALLEL SOLUTIONS
4.GREATER LEVEL OF EFFICIENCY WITH SCALABLE LOAD
5.REDUCTION OF FAILURE DURING MAINTENANCE / SUPER-FAST REPLACEMENT (MTTR)
6.LOWER COST OF BATTERIES
7.LOWER COST OF REPAIR
8.GET MORE POWER FROM SAME INFRASTRUCTURE
9.LOWER COST OF OWNERSHIP OVER LIFETIME
10.DELIVERY, OFFLOADING AND POSITIONING
Q4: What is difference between offline UPS and online UPS?
1. Power Supply Mode
Online UPS
Always powered by the inverter: Regardless of whether the grid is normal or not, the load is powered by the UPS’s internal inverter, and the grid only charges the UPS or serves as a backup energy source.
Grid → rectifier → inverter → load: This forms a closed-loop power supply chain, completely isolating the system from grid fluctuations.
Offline UPS
Directly powered by the grid during normal operation: When the grid is stable, the load is directly powered by the mains, and the UPS is in “standby” mode, charging its batteries only.
Switch to inverter during power outages: Only when the grid is abnormal does the inverter start to power the load.
2. Transfer time
Online UPS: Transfer time is 0ms (uninterruptible power supply), as it always operates through the inverter, eliminating the need for a switchover process.
Offline UPS: Transfer time is approximately 4-10ms, depending on the response speed of the electronic switch, which may cause a brief power outage (posing a risk to IT equipment).
3. Output
Online UPS
Outputs a pure sinusoidal wave with high voltage and frequency stability (e.g., voltage fluctuation ≤ ±2%, frequency fluctuation ≤ ±0.1Hz).
Built-in filtering and voltage stabilization functions suppress grid interference such as surges, harmonics, and voltage drops.
Offline UPS
Outputs a mains waveform during normal operation and a square wave or quasi-sine wave after a power outage, resulting in poor power quality (which may cause equipment overheating or malfunction).
Provides only basic filtering and weak protection against grid interference.
4. Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Online UPS
Efficiency is approximately 92%-96% (at a load factor of 40%-70%), but because the inverter is always running, standby losses are higher.
Eco mode is supported, switching to bypass power when the grid is stable, achieving efficiency exceeding 98%.
Offline UPS
Efficiency is close to 100% during normal operation (directly powered by mains power), but the inverter only operates during power outages, resulting in lower overall energy consumption (suitable for low-power scenarios).
5. Applications
Online UPS
High-reliability scenarios: Data centers, hospital operating rooms, financial trading systems, industrial control systems, etc., requiring zero-interruption protection.
Sensitive electronic equipment: Servers, precision instruments, communications equipment, etc., requiring high-quality power supply.
Offline UPS
Small, non-critical equipment: Home computers, printers, small-scale office networks, etc., requiring only short power outages (e.g., a few minutes).
Budget-constrained scenarios: Suitable for individuals or small and micro businesses as a basic backup power solution.
6. Cost and Maintenance
Online UPS
Initial cost is high (3-5 times the price of a backup UPS), and regular maintenance is required for components such as the inverter, battery, and fan.
It has a longer lifespan (designed for 10-15 years) and supports modular replacement components.
Offline UPS
They are low-cost (typically under 1,000 yuan) and require minimal maintenance (only regular battery checks are required).
They also have a short lifespan (5-8 years), and most are integrated, making them difficult to repair if they fail.
Choice Recommendations:
If your equipment cannot tolerate any power outages or power interruptions (such as a data center), you must choose an online UPS.
If you only need basic power outage protection (such as temporarily saving documents) and your budget is limited, consider a offline UPS.
Q5: What is a voltage stabilizer?
A power supply voltage stabilizer is a power supply circuit or device that automatically adjusts its output voltage. Its function is to stabilize power supply voltages that fluctuate widely or are unsuitable for electrical equipment within its set range, ensuring that various circuits and electrical equipment operate normally at their rated operating voltage.
Voltage stabilizers are widely used in industrial and mining enterprises, oil fields, railways, construction sites, schools, hospitals, postal and telecommunications facilities, hotels, and scientific research facilities, where stable power supply voltage is required, including computers, precision machine tools, computed tomography (CT) scanners, precision instruments, testing equipment, elevator lighting, imported equipment, and production lines. They are also suitable for users at the end of low-voltage distribution networks experiencing low or high power supply voltage fluctuations, as well as for electrical equipment with highly variable loads. They are particularly suitable for all applications requiring high voltage waveform stability. High-power compensating power voltage stabilizers can be connected to thermal, hydraulic, and small generators.
A power regulator consists of a voltage regulator circuit, a control circuit, and a servo motor. When the input voltage or load changes, the control circuit samples, compares, and amplifies the signal. It then drives the servo motor, causing the position of the regulator’s carbon brushes to change. This automatically adjusts the coil turns ratio to maintain a stable output voltage. Larger AC voltage regulators also utilize the principle of voltage compensation.
Features:
1. Wide input voltage range accommodates wide variations in vehicle battery voltage.
2. High-efficiency supercapacitors combined with a switching power supply system provide smooth and intelligent operation, effectively protecting the vehicle battery.
3. Stable voltage output eliminates the effects of voltage fluctuations caused by battery and cable internal resistance during high dynamic operation, allowing the audio/video system to operate stably at the high end of the rated voltage range, maximizing the amplifier’s power output and dynamic range.
4. Low ripple output effectively suppresses power supply noise interference.
5. Low impedance and strong transient dynamic response ensure powerful bass, rich midrange, and clear treble. Power requirements.
6. High power (360W at 12V input), sufficient for all standard car audio and video systems with up to six channels.
7. High efficiency (switching frequency 200kHz), low power consumption, quiet operation, low heat generation, no fan, no ACC control required, compact size, light weight, easy installation, and maintenance-free operation.
8. Comprehensive protection features: self-resetting input undervoltage protection; self-resetting input overvoltage protection; input current limit protection; output overvoltage protection with latching (power-off reset); self-resetting output short-circuit protection; and output soft-start.
