NEWS DETAILS
What is an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) and why do you need it?
In today’s digital drive world, power interruptions is not only an inconvenience, but also leads to data loss, hardware damage and long-term operation downtime. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, the annual loss caused by power outages to the U.S. economy is estimated at 150 billion dollars. This is the essential place of Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS). In essence, a UPS is a kind of equipment that provides emergency power for the load when the input power (usually the main power grid) fails. But its role extends beyond just being a backup battery; It provides important protection against all kinds of abnormal power supply.

Understanding the Core: what is a UPS?
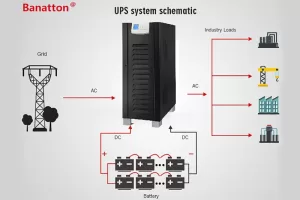
Uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is an electrical equipment, which can provide instantaneous power supply when the main power supply fails. The main function of any UPS is to build a bridge between a power failure and starting auxiliary power supply (such as generator), or to provide enough time for an orderly closing connected equipment. There are many types of UPS systems, but for computing and network equipment, the two most common ones are standby UPS and UPS which is usually called standby UPS.
A Standby UPS, also known as an Offline UPS, is the most basic type. It allows connected devices to run directly from the mains until a problem is detected. When a power failure, voltage sag or power surge occurs, it will switch to battery power supply quickly (within a few milliseconds). This type has low cost, and is very suitable for protecting personal computers, routers and other non-critical equipment. On the other hand, a more robust Backup UPS often incorporates online or line-interactive technologies, offering a higher level of protection. It continuously adjusts the input power supply and provides seamless battery backup, making it suitable for more sensitive equipment such as small servers and workstations.
Main advantages and product specifications.
The unique advantage of a modern computer UPS lies in its intelligent design, which far exceeds the simple battery backup. International standards such as IEC 62040-3 define the performance and test requirements of uninterruptible power supply systems, ensuring its reliability and security [ International Electrotechnical Commission. “IEC 62040-3: Uninterruptible power systems (UPS) – Part 3: Method of specifying the performance and test requirements.” https://www.iec.ch/]. Let’s break down the key performance indicators that define high quality unit.
- Intelligent control and Management: excellent microprocessor control optimizes the reliability of the system, while an intelligent battery management system extends the battery life. A built-in super smart charger, significantly shortening the charging time.
- Advanced power supply regulation: the functions of step-up and step-down automatic voltage regulation (AVR) can stabilize voltage without switching to battery, thus prolonging the battery life. The device outputs an analog sine wave, which is compatible with most electronic equipment.
- Enhanced availability and security: The Functions of automatic restart, self-test and built-in self-diagnosis Functions when AC power is restored ensure smooth operation. An off-mode charging function allows the battery to be charged even when the device is turned off. A humanized alarm system provides clear status updates.
- Flexibility and compliance: UPS is compatible with generator sets, and provides optional functions, such as no-load shutdown and monitoring of RS 232/USB communication ports. It carries a CE certificate (No.: m.2021.206.C 67628) to confirm that it conforms to the European health, safety and environmental protection standards.
Where can I use UPS? Important application scenarios
Uninterruptible power supply systems is widely used and important in various fields.
- IT and Networking: Computer UPS protect small servers, workstations, routers, switches, and network-attached storage (NAS) from data corruption.
- Monitoring and safety: ensure that monitoring equipment, DVR and NVR keep running during the power failure.
- Industrial Automation: protect key systems, such as ATM, ticket vending machine (TV), SCADA systems and railway signal systems, etc.
- Office Environments: Providing backup for PCs, printers, scanners, Point-of-Sale (POS) systems, telephones, and fax machines.
FAQ
Q 1: What are the meanings of 3/1, 1/1, 1/3 and 3/3 in input/output stage?
A 1: This indicates the electrical phases. For example, 3/1 indicates three-phase input and single-phase output (380 v to 220 v), which provides convenient output wiring. Similarly, 1/1 is standard single-phase input and output (220 v to 220 v), and 3/3 is three-phase input and output (380 v to 380 v)
Q 2: Why does the Uninterruptible Power Supply need grounding?
A 2: Earthing is an important safety feature. First of all, the high voltages inside UPS means that if it is not grounded, the failure could electrify its metal shell, causing serious security risks. Second, the correct grounding ensures the voltage stability between neutral wire and ground wire, and prevents the sensitive connection equipment from failing.
Q 3: Can a switch be connected to the grounding wire?
A 3: absolutely not. A switch on the ground wire violates the safety regulations. If the switch fails, the grounding connection will be disconnected, which can lead to the risks of electric shock death and introduce electrical noise that interferes with the operation of the equipment.
Related Articles
The Power of Modular UPS Systems in Commercial Infrastructure
What is an industrial UPS?—How to choose an industrial UPS?
The Development of Voltage Stabilizers
Posts Categories
- News16