NEWS DETAILS
UPS Backup Batteries: Protecting Healthcare Facilities
In the healthcare industry, time is of the essence. Healthcare professionals rely heavily on cutting-edge technology to provide patients with accurate diagnoses and optimal treatment, whether for routine checkups or potentially life-saving surgeries. As this technology becomes increasingly complex in the modern digital age, the need for continuous power supply becomes absolutely essential.
Imagine the consequences if diagnostic equipment suddenly stops working due to a power surge, or if a hospital experiences a power outage during a life-saving surgery. These events can be not only fatal but can also lead to costly downtime, data loss, and equipment damage. Healthcare facilities use uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems to avert these catastrophic events.
This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need about uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) for medical equipment, including how they work, important features to be aware of, and best installation methods. If you want to understand how uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems help healthcare facilities operate smoothly and keep patients safe, this article will provide a detailed overview.
1. The Importance of UPS Backup Batteries in Healthcare Environments:
In complex and high-risk medical settings, accuracy and reliability are paramount. MRI machines, life-saving ventilators, and essential cardiac monitors rely on a continuous power supply. Even brief power outages or voltage fluctuations can lead to patient injury, equipment malfunction, and loss of critical medical data.
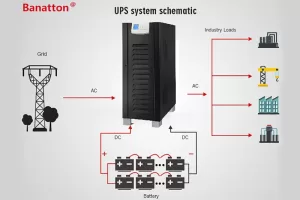
Now we have uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, a critical technology ensuring the smooth operation of healthcare systems. A UPS acts like a vital electricity insurance policy; it is always ready to provide continuous and rapid backup power in the event of a power outage or other disruption.
This technology guarantees healthcare institutions the ability to provide continuous patient care and protect the integrity of valuable medical data, which is more important than mere continuity. An underrated hero in time-sensitive fields, UPS systems consistently protect vital patient records, enabling physicians to provide optimal treatment.
2. Critical Medical Equipment Powered by UPS Backup Batteries:
In the intricate network of healthcare, UPS systems appear as critical nodes, strategically connecting a range of indispensable medical devices. At the heart of their importance lies their role as an insurance mechanism, protecting equipment that is not only essential to patient care but also highly dependent on a stable power supply.
Ventilators maintain respiratory function, and their ally is the stable power provided by a UPS. Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitors regulate the subtle rhythms of life, safeguarding uninterrupted energy. The seamless operation of infusion pumps, responsible for precise and controlled drug delivery, relies on the continuous power supply provided by a UPS. Furthermore, critical medical equipment includes diagnostic imaging devices such as MRI machines, CT scanners, and X-ray machines, whose results are directly proportional to power stability.
Even complex networks of meticulously orchestrated, critical testing and analysis equipment require robust UPS support to ensure seamless and reliable operation. It must be recognized that the importance of a UPS extends beyond this incomplete list; it protects a complex network of equipment that collectively ensures the health and well-being of patients receiving medical care.

3. Choosing a UPS Backup Battery System Suitable for Medical Needs:
Selecting the right UPS for your medical equipment directly impacts patient safety and the smooth operation of your healthcare facility. To make an informed decision, you need to consider the following important factors:
- Battery Life and UPS Power Supply: Before connecting any medical equipment to a UPS, you must first determine its power requirements (watts). This is known as load-size assessment. Choosing a UPS with a voltage ampere (VA) or watt (Watt) rating is based on this careful assessment.
- Uptime Determination: Calculate how long medical equipment can operate on batteries alone during a power outage. The UPS battery capacity needed to meet your unique needs will be determined by this assessment.
- Future Expansion Strategy: Consider UPS capacity to account for future equipment additions to your healthcare facility. Purchasing a slightly larger UPS system in advance is generally more economical than replacing it later as the facility expands.
- Reliability and Scalability: Before implementing a UPS system, consider the importance of redundancy. Setting up multiple UPS systems provides additional protection. Redundancy ensures that a second device can easily take over in case of a UPS failure, preventing power outages for medical equipment.
Ensure that your chosen UPS system can expand as your healthcare facility grows to meet your increasing needs. The evolving needs of healthcare operations can be easily met by scalable UPS systems that can be upgraded with increased battery capacity or UPS equipment as needed. - Emergency Preparedness: UPS backup batteries are the cornerstone of healthcare continuity planning. In the ever-evolving healthcare landscape, emergency preparedness is paramount. Explore how UPS backup battery systems serve as the cornerstone of healthcare continuity planning, ensuring a seamless transition during power outages and other emergencies.
- Outage Response: UPS systems demonstrate exceptional agility in responding to power outages or utility interruptions. Upon detecting a power interruption, they switch to battery power almost instantly. This switch is completed within milliseconds, ensuring uninterrupted power supply to connected medical equipment. In hospital environments, even milliseconds of power outages can have catastrophic consequences, making this immediate response crucial.
- Inverter Function: The inverter is a core component of the UPS system and plays a critical role during power outages. This component is responsible for converting the direct current (DC) from the battery to alternating current (AC), the standard current used by most medical devices. This conversion is essential to ensuring that medical equipment continues to function even during power outages.
- Battery Life: The battery life of a UPS depends on the load it handles and the duration of the potential outage. Depending on the battery type and capacity, the duration of a UPS is typically measured in volt-amperes (VA) or watts (W) and can vary significantly. Therefore, these factors are crucial for healthcare providers and institutional managers when selecting a UPS system.
Related Articles
The Power of Modular UPS Systems in Commercial Infrastructure
What is an industrial UPS?—How to choose an industrial UPS?
The Development of Voltage Stabilizers
Posts Categories
- News23