NEWS DETAILS
What is an industrial UPS?—How to choose an industrial UPS?
An industrial UPS is a device that provides temporary power to large electrical equipment during power outages. Because it uses three-phase power, which is common in industrial environments, it is called an industrial UPS.
1. What is an industrial UPS?
An industrial UPS is a special type of uninterruptible power supply used primarily to protect industrial equipment and systems, preventing downtime and data loss. It typically requires high reliability, quality, and efficiency, and must be able to withstand harsh industrial environments and a wide range of operating temperatures.
2. Types of Industrial UPS:
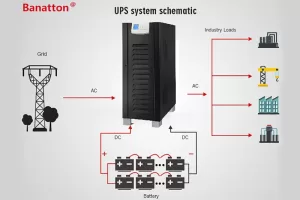
There are many types of industrial UPSs, and the most common industrial UPSs include DC UPS, three-phase input, single-phase output UPSs, and three-phase input, three-phase output UPS.
3. Functions of UPS:
UPS systems have two specific functions:
1. Voltage Stabilization: This regulates voltage fluctuations between the incoming mains power and the start-up of the generator. This is also commonly known as voltage stabilization. When the supply voltage fluctuates unsteadily and falls below the rated voltage, the UPS automatically adjusts the output voltage to the rated voltage. In China, the three-phase industrial voltage is 380V.
2. Power Outage Continuity: In the event of a grid power failure or outage, the UPS activates a backup power source to continue powering the load equipment, allowing the equipment to continue operating.
4. When selecting an industrial UPS, consider the following factors:
1. Power Capacity:
Power capacity determines how many load devices a UPS can power. Higher power means more devices can be powered. When selecting a UPS system, ensure adequate capacity. During initial purchase, calculate the total maximum power draw of the load devices requiring UPS power. Insufficient UPS system capacity can cause the entire system to malfunction, resulting in significant cost savings.
2. Battery Life:
Battery life refers to how long a UPS can provide power to load devices in the event of a power outage. This duration is determined by the battery capacity of the UPS system. Industrial UPS batteries are typically external. Manufacturers configure batteries of varying capacities based on user needs. Currently, battery life ranges from 5 minutes to several hours.
3. UPS System Maintenance:
UPS systems utilize electrochemical energy stored in a battery, typically a string of valve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA) batteries. It’s recommended that these systems have quarterly battery maintenance and battery replacement every four to eight years. While these precautions ensure the proper functioning of the UPS and batteries, they can also backfire, as human error is the primary culprit behind most site failures. Conversely, UPS systems offer short-term power and are an alternative to traditional battery storage. Compared to battery-based options, they require less maintenance and have no replacement cycles.
4. Total Cost:
While system performance, runtime, reliability, and maintenance are important factors to consider, many purchasing decisions ultimately come down to a simple question: How much will this cost me?
When selecting a UPS, it’s important to remember that the product with the lowest initial cost may not always be the best long-term solution. Traditional battery-based UPS systems require frequent maintenance, battery replacement cycles, space, and regulated ambient temperatures, all of which can result in higher costs.
UPS solutions offer higher operating efficiency, lower maintenance and cooling requirements, and no battery replacement costs, resulting in a lower total cost of ownership. Furthermore, since these units lack battery cabinets, they occupy significantly less floor space.
Related Articles
The Power of Modular UPS Systems in Commercial Infrastructure
The Development of Voltage Stabilizers
What makes uninterruptible power supply indispensable to modern electrical equipment?
Posts Categories
- News16